Common names such as powder, powder, and dry powder are different, but they actually represent the same meaning, with different expression habits in our work.
Due to the diversity of powder characteristics, seemingly simple powder mixing processes often encounter problems of one kind or another. Some problems have complex causes, resulting in the inability to achieve uniform mixing. Ultimately, it will reduce the product quality of downstream products of the powder, and even result in product scrapping. These phenomena have attracted high attention from our team, and we are determined to study powder mixing technology well to provide technical services to our customers. We have compiled this powder mixing technology Q&A encyclopedia for this purpose, hoping to solve some practical problems for you.
In the face of the aforementioned thorny issues, we will analyze and determine the specific reasons that affect the uniformity of mixing from the following aspects.
1、 The three major characteristics of powder are the basis for studying powder mixing
Before finding the cause of uneven powder mixing, it is necessary to understand the three major characteristics of the powder.
1. Specific gravity (density) of powder
Due to the different loose and tight states of the powder, it can be divided into the following three specific gravity:
1) Loose specific gravity
2) Vibration specific gravity
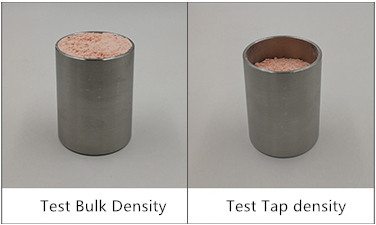
3) Free stacking specific gravity
Free stacking specific gravity refers to the actual stacking specific gravity of materials or the stacking specific gravity of materials in the mixing machine barrel. The free bulk density is between the loose bulk density and the compacted density.
For detailed information, please refer to Topic 2 of the Powder Mixing Encyclopedia.
2. Particle size of powder (particle size)
The particle size of the powder is also an important factor affecting powder mixing, and the differences may be significant during mixing work, such as salt particles of about 0.6mm and pigment particles of about 0.001mm. The greater the differentiation, the more difficult it is to mix evenly.

3. Flowability of powder
The flowability of powder is also an important characteristic, as good or bad flowability can affect the result of uniform mixing. For detailed information, please refer to Topic 4 of the Powder Mixing Encyclopedia.

The above three major characteristics are the foundation of our research on powder mixing technology. Most of the problems encountered in mixing are caused by the simultaneous occurrence of one or more characteristics. The method of analyzing problems is based on these three major powder characteristics.
2、 The greater the difference in the characteristic values of the powders involved in mixing, the more difficult it becomes to mix
Research has found that the smaller the difference in characteristic values of various powders in the material to be mixed, the easier it is to mix evenly, while the larger the difference in characteristic values of powders, the harder it is to mix evenly.
1. For example, mixing large particle size powders with small particle size powders can be difficult to achieve even mixing.

2. For example, it is difficult to mix a powder with a larger weight and a powder with a lighter weight evenly.

The greater the differentiation mentioned above, the more difficult it becomes to mix evenly.
For detailed information, please refer to questions 14 and 15 of the Powder Mixing Encyclopedia.
3、 The more extreme the characteristic values of the powder involved in mixing, the less likely it is to mix evenly
Research has found that the characteristic values of the powders involved in mixing are near the middle value, making it easy to achieve uniform mixing. If its characteristic value is too high or too low, it will bring mixing difficulties, and the more extreme the characteristic, the more difficult it is to mix.
Extremely heavy or light specific gravity (heavy or light powder) can cause difficulty in mixing.

2. Extremely large or small particle sizes (large or fine powder) can also cause mixing difficulties.
3. Poor or excessive liquidity can cause mixing difficulties.
Detailed answers to the above questions in the Encyclopedia of Powder Mixing Questions 15, 16, 5, and 6.
4、 Difficulties in mixing caused by other special characteristics of the powder to be mixed
Some powders may have difficulties in mixing due to moisture, excessive viscosity, presence of difficult to disperse pseudo particles, and presence of fibrous bundles.
The solution is to perform corresponding pre-treatment for such powders before mixing. For detailed information, please refer to Topic 7 of the Powder Mixing Encyclopedia.
Dual motion can be used for powders containing fibrous bundles and pseudo particles ® The flying knife dispersion mixer uses high-speed rotating flying knives to disperse its binding force, as detailed in Topic 24 of the Powder Mixing Encyclopedia.
5、 Targeted mixers should be selected based on the problems existing in the powder to be mixed
We need to choose an appropriate mixer to overcome the problems in the characteristics of the powder to be mixed.
1. For example, for food powders with poor fluidity (such as flour, chili powder, and plant fiber powder), we need to choose a mixer with a forced shear function to forcibly mix the materials to overcome the mixing difficulties caused by insufficient fluidity.
2. For materials containing light powder and ultra light powder (such as plant fiber powder, nano powder, etc.), double movement is required ® Mixer, utilizing dual motion ® The mixer has a clamping function of bucket movement and blade movement to overcome the difficulty of light powder floating and difficult mixing.